If you or a loved one is about to undergo joint replacement surgery, this guide will help you understand what to expect, what doctors may not tell you, and how physiotherapy can make your recovery faster and more effective. Joint replacement surgery is a life-changing procedure for anyone and knowing what to expect can help reduce anxiety!
What is Joint Replacement Surgery?
Joint replacement surgery involves removing the damaged joint and replacing it with an artificial one. The most common types of joint replacement surgeries include:
- Knee Replacement
- Hip Replacement
- Shoulder Replacement
What Happens After Surgery?
Many patients believe that once the surgery is done, they will be pain-free and walk normally in a few days just like that. However, recovery takes time and effort. Here’s what happens after surgery:
1. Pain and Swelling
After surgery, pain and swelling are common. The body needs time to heal. Doctors will prescribe pain medications, but managing pain through physiotherapy is equally important.
2. Limited Movement
Your new joint will be stiff, and you may not be able to move it freely. Walking, bending, or even standing for long periods may be challenging initially.
3. Use of Assistive Devices
You may need a walker, crutches, or a cane for a few weeks to help with walking and balance. You literally have to learn to walk again!
4. Physiotherapy Begins Early
Physiotherapy usually starts within 24 hours of surgery. Your physiotherapist will guide you through gentle movements to prevent stiffness and improve circulation.
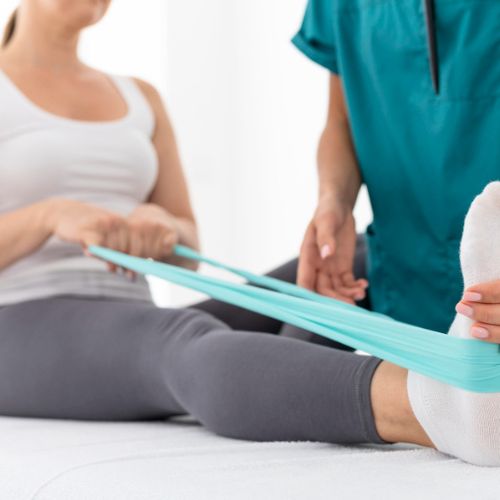

The Role of Physiotherapy in Recovery
Physiotherapy is the most crucial part of the recovery process. It is the make or break factor deciding the success rate of the patient post-surgery. Physiotherapy helps you regain strength, mobility, and confidence in using your new joint. Here’s how it helps at different stages:
1. Pre-Surgery Physiotherapy (PREHAB)
Doctors may not always emphasize the importance of physiotherapy before surgery, but it makes a big difference in recovery. Prehabilitation includes:
- Strengthening exercises for muscles around the affected joint.
- Flexibility training to improve movement.
- Balance exercises to prepare for post-surgery mobility.
- Breathing exercises to improve lung function for surgery.
A stronger body before surgery recovers faster afterward.
2. Early Post-Surgery Physiotherapy (Hospital Stay)
Your physiotherapist will help you with:
- Gentle Joint Movements – To reduce stiffness.
- Breathing Exercises – To prevent lung infections after anesthesia.
- Movement Training– focuses on how to go to the toilet, how to turn in bed, how to sleep etc.
- Walking Training – Using crutches or a walker.
- Pain Management – Ice therapy and gentle exercises to reduce pain.
3. Home Physiotherapy (First 6 Weeks)
Once discharged from the hospital, recovery continues at home. Physiotherapy will focus on:
- Increasing Joint Movement – Stretching and bending exercises.
- Building Strength – Strengthening surrounding muscles to support the new joint.
- Walking & Balance Training – Improving mobility without assistive devices. This component is the most crucial and has been given most importance for recovery especially after knee replacement surgery. Read more –https://tinyurl.com/4k639wsm
- Pain Relief Techniques – Using heat, ice, or gentle massage.
4. Advanced Physiotherapy (3-6 Months After Surgery)
As recovery progresses, exercises become more intense to restore full function. This phase includes:
- Functional Training – Practicing daily activities like climbing stairs, getting in/out of a car, or squatting.
- Endurance Exercises – Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling to improve stamina.
- Sports Rehabilitation – For active individuals who want to return to sports.
Many patients are surprised by certain aspects of recovery. Here are a few things doctors may not always mention:
What Doctors Don’t Always Tell You
1. Recovery Takes Time
While many believe they’ll recover in a few weeks, full recovery can take 6 months to a year, depending on age, health, and commitment to physiotherapy.
2. Pain and Stiffness May Last for Months
Even with surgery, mild discomfort and stiffness can persist for several months. Regular physiotherapy helps minimize this.
3. Your Other Joints Will Work Harder
After surgery, your body adjusts to the new joint. Other joints, like the lower back, opposite knee, or hip, may feel extra strain. Strengthening exercises can prevent future joint problems.
4. Muscle Weakness is Common
After surgery, muscles around the joint may feel weak. Physiotherapy helps restore muscle strength over time.
5. Fear of Movement is Normal
Many patients are afraid to move too much, worrying they might damage the new joint. However, movement is essential for recovery. Your physiotherapist will guide you on safe exercises.
Read importance of balance exercises here – https://tinyurl.com/mmzpaf78
Tips for a Smooth Recovery
Here are some practical tips to recover faster and regain independence after joint replacement surgery:
1. Follow Your Physiotherapist’s Plan
Commit to daily exercises and follow instructions carefully to regain mobility faster.
2. Stay Active but Don’t Overdo It
Gradually increase activity but avoid overexertion. Too much strain can slow down healing.
3. Eat a Healthy Diet
Nutrients like protein, calcium, and vitamins help with healing and strengthening muscles.
4. Manage Pain Naturally
Ice therapy, gentle stretching, and relaxation techniques can help reduce pain without over-relying on medications.
5. Use Assistive Devices Properly
Using crutches, a walker, or a cane correctly can prevent falls and unnecessary strain.
6. Be Patient
Recovery is a journey. Stay positive and trust the process.
Take-away Message
Joint replacement surgery can give you a new lease on life, but a successful recovery depends on physiotherapy. Starting exercises early, staying committed to therapy, and being patient with progress can help you regain strength and confidence. If you or a loved one are preparing for joint replacement, remember—physiotherapy is your best ally on the road to recovery!
Dr. Neha Gogate-Kulkarni (PT)
Rehab Station